Diverticulitis: Diet, Symptoms, Treatment, Foods to Avoid
Diverticulosis is a condition in which the inner lining layer of the large intestine or colon bulges out (herniates) through the outer, muscular layer. These ‘outpouchings’ are called diverticula.
Diverticulitis is the term for inflammation and infection in one or more diverticula.

A person having diverticulosis (the condition), and perhaps diverticulitis (the inflammation) as well, is said to have diverticular disease.
Diverticulosis Symptoms, Causes, & Treatment
Diverticula occur in a colon weakened by age when increased pressure inside the colon (usually due to constipation) causes little pea-shaped pouches of weakness in the intestine wall.
The chance of developing diverticula increases with age, so that by age 50 between 20 and 50 percent of all people will have some diverticula, and by age 90 virtually everyone will.
Symptoms
Diverticulosis is usually symptom-free so most people do not realize they have it. However, a few people will experience cramps, spasms, constipation, and pain.
Treatment
Relieving constipation, primarily by increasing fiber in the diet, can reduce the problems associated with diverticulosis. If cramps, bloating, and constipation are a problem, a doctor may prescribe a short course of pain medication. However, many medications cause the colon to empty, an undesirable side effect for people with diverticulosis.
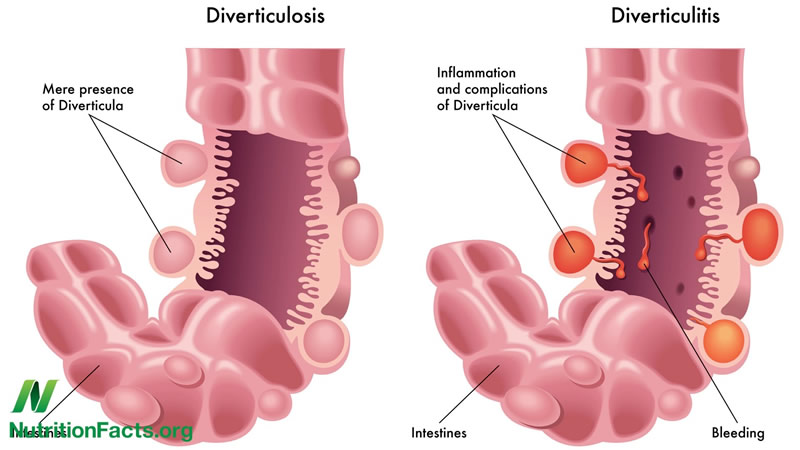
Diverticulitis Symptoms, Causes, & Treatment
A person with diverticulosis may get diverticulitis when waste matter and bacteria are trapped in a pouch (diverticula).
This blockage interferes with the blood supply to the area, and infection sets in.
The tissue then becomes inflamed or infected, and in severe cases may even rupture. An attack of diverticulitis can result in fever, pain, and tenderness around the left side of the lower abdomen.
Symptoms
The infection and irritation of nearby tissues within the abdomen may cause the abdominal muscles to spasm. About 25 percent of all patients with diverticulitis will have some rectal bleeding although this rarely becomes severe. Diverticulitis is three times more likely to occur in the left side of the large intestine, and men are three times as likely as women to suffer from diverticulitis.
Treatment
Treatment for diverticulitis focuses 3 areas.
- Clearing up the infection and inflammation with antibiotics.
- Resting the colon with a liquid diet plus a pain reliever or a drug such as propantheline (Pro-Banthine) to control muscle spasms.
- Preventing or minimizing complications with the proper diet.
Acute or repeated attacks with severe pain or severe infection may be serious enough to require a hospital stay and possibly surgery.
High Fiber Diet Recommendations
High Fiber Diet for Diverticular Disease
This diverticulitis diet is a high fiber diet for managing diverticulosis, and for reducing effects of diverticulitis. The increased fiber (the American Dietetic Association recommends 20 to 35 grams daily, including 6-8 grams of soluble fiber) in this diverticulitis diet plan produces more bulk in the stool, reducing pressure in the colon and assisting the more regular and complete elimination of waste, thereby preventing the formation of further diverticula.
Build up consumption of fiber in your diet gradually – rapid fiber increase may result in gas, cramping, bloating, or diarrhea.
There are benefits of having different kinds of fiber in a balanced diverticulitis diet:
- It helps to protect against cancer of the colon and rectum.
- It assists in preventing heart disease and a number of other health problems.
- Foods containing fiber also tend to comprise nutrients like vitamins A, C, and E as well as selenium which is useful in fighting cancer.
Increase Fluid and Fiber
Anyone with diverticulitis who increases their fiber intake under this diverticulitis diet plan, should drink at least 1.5 liters (3 pints) daily. Insoluble fiber needs fluid to form stools that are easily passed.
Medical advice may be to take a fiber supplement such as Metamucil daily (for soluble fiber from psyllium), and to use a cholesterol-lowering spread or margarine containing plant sterols. Fiber supplements provide about 2 to 3.5 grams of fiber per tablespoon, which is mixed with a quarter liter (8 ounces) of water before consuming.
Should Seeds Be Eaten?
Until recently, many doctors suggested avoiding foods with small seeds because it was believed that particles could lodge in the diverticula and cause inflammation. However, this is now a controversial point and no evidence supports this recommendation.
The seeds in tomatoes, zucchini, cucumbers, strawberries and raspberries, as well as poppy seeds, which are part of your diverticulitis diet, are generally considered harmless.
Diverticulitis Diet Guidelines
Foods to Eat
| Grains |
|
| Vegetables |
Eat raw or dried fruits and raw vegetables if possible – chopping, peeling, cooking, pureeing, juicing, and processing fruit and vegetables may reduce fiber content. |
| Fruit |
|
| Milk/Dairy |
|
| Meat/Meat Substitutes |
|
| Fats and Snacks |
|
Foods to Avoid
Any hard or difficult-to-digest foods such as;
- nuts
- corn
- popcorn hulls
- sunflower seeds
- pumpkin seeds
- caraway seeds
- sesame seeds
Questionable foods
- stringy fiber foods like sweet potato
- strawberries
- kiwi fruit
- raspberries
- blackberries
See Also
This page is not meant to diagnose or treat disease. Consult a medical professional if experiencing the symptoms listed or before starting any dietary guidelines suggested on this page.
References
- Wong, W. D., Wexner, S. D., Lowry, A., Vernava III, A., Burnstein, M., Denstman, F., ... & Simmang, C. (2000). Practice parameters for the treatment of sigmoid diverticulitis—supporting documentation. Diseases of the colon & rectum, 43(3), 290-297. link
- Ambrosetti, P., Robert, J. H., Witzig, J. A., Mirescu, D., Mathey, P., Borst, F., & Rohner, A. (1994). Acute left colonic diverticulitis: a prospective analysis of 226 consecutive cases. Surgery, 115(5), 546-550. link
- Ferzoco, L. B., Raptopoulos, V., & Silen, W. (1998). Acute diverticulitis. New England Journal of Medicine, 338(21), 1521-1526. link
slippery elm and marshmallows root are two natural supplements to improve a diverticulitis attack. Do some research and see it for yourself. Good luck
I urge all who have bouts of diverticulitis to read “Diverticulitis Diet Guide” by Monika Shah. It has changed my life. It’s short & concise with a list of what not to eat. I have given up red meat & fried food and the results have been spectacular. Also, any gas producing veggies are not our friends. No beans or anything in the Cruciferous vegetable family. I hope it gives you the peace & health it’s given me.
I’ve listened for 15 minuets and still don’t know what 3 foods to avoid, this is total BULL SHIT..
What about pineapples?
Can we have been dip
been or bean?
Can have seedless Smuckers strawberry jam? What about raisins like raisin cinnamon bread?an. And grilled Charles burgers and chicken is that okay?
There seem to be conflicting recommendations re berries and
nuts. Nuts are good for fiber intake but difficult to digest (cf.
diverticulitis); raspberries and strawberries, while beneficial in
this regard are also small-seed “villains”–opinion?
Can taco shells for corn or do I need to eat flour tortillas
Ground corn products are probably fine. It’s the whole kernel corn products that should be avoided.
Would apple butter be OK on wheat toast, orange juice, any kind of kids cereal or just bran cereals to eat,
What about sweets, pie, pop tarts, cereal bars, are they oknow to eat.
Many of the things on this diet are no good for those of us with IBS. Any suggestions??
My daughter-in-law has diverticulitis and had a perferated colon, had surgery to remove part of colon. While she is wearing a colonoscopy bag, What is best for diet. How to avoid constipation. I advised small meals, 5-6 x a day, but she is having trouble.help.
She really should consult her physician for recommendations.
spinach with kale, carrots, apples and banana with coconut water. stir in blender and drink. Plenty of nutrients and fiber. In addition research about slippery elm and marshmallow root. Doctors are very confused when it comes to nutrition. And sadly to say, most dieticians learned old and antiquated hoaxes that were spread during the mid 1980’s. Schools in the US still teaching a lot of non-sense about diet and nutrition which have contributed to the misinformation on the obesity, diabetes and heart disease epidemics.